ETL 1110-1-183
1 Apr 98
system through the following relation:
at the node points of a regular grid (i.e., a 2' x 2' grid
spacing). Biquadratic interpolation procedures can be
used within a grid cell boundary to approximate the geoid
h=H+N
height at a given geodetic latitude and longitude. The
where,
h = ellipsoid height
NGS GEOID96 model for the United States indicates
H = orthometric height
geoid heights range from a low of -51.6 meters in the
N = geoid height,
Atlantic to a high of -7.2 meters in the Rocky Mountains.
For more information on geoid modeling, see Milbert
and by convention N being a positive height above the
(1996).
ellipsoid.
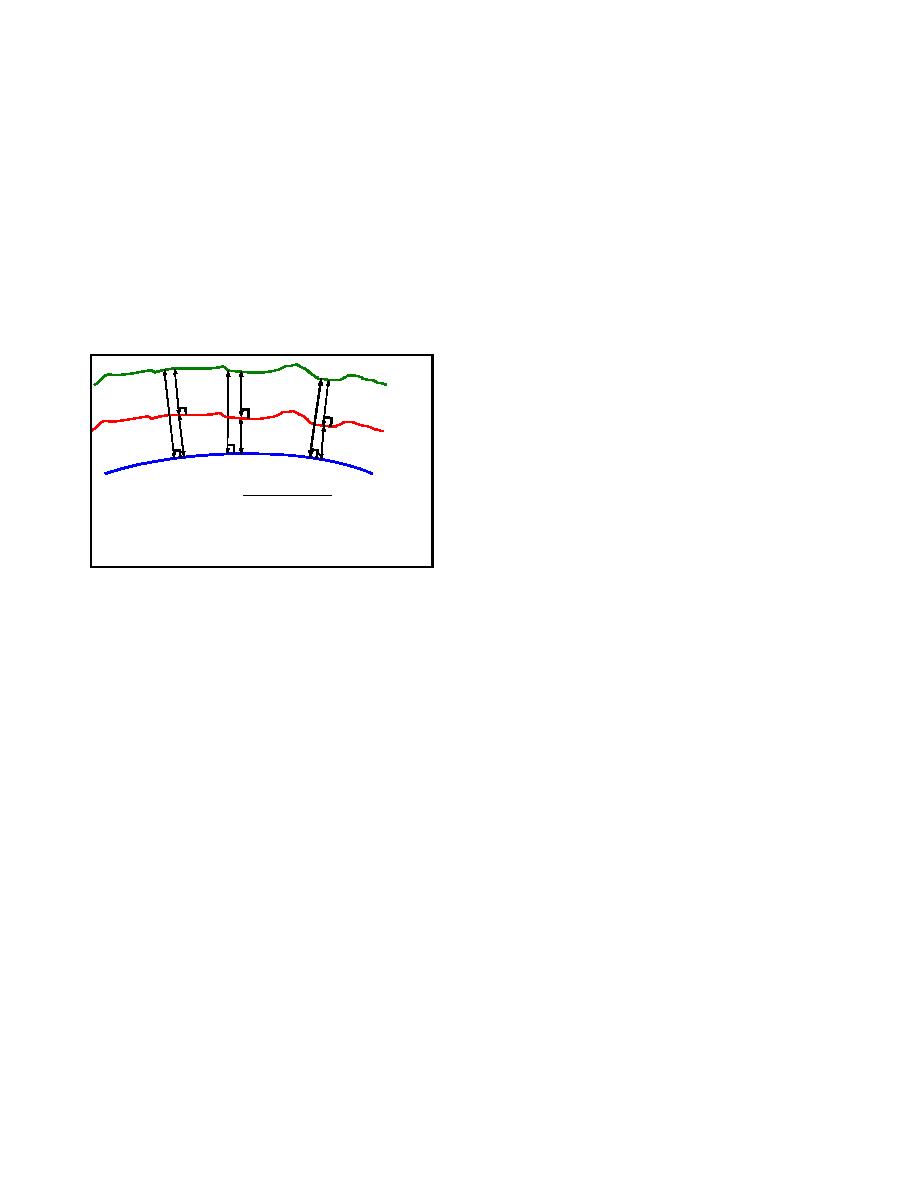
EARTH SURFACE
A-4.
Relative Vertical Positioning with GPS
A
B
H
a. DGPS observation sessions produce 3-D geodetic
h
GEOID
coordinate differences that establish the baseline between
N
two given stations. Baseline solutions produce relative
ELLIPSOID
positioning results at a greater accuracy than can now be
achieved from point positioning. The expected accuracy
H = ORTHOMETRIC HEIGHT
Differencing Technique:
of such ellipsoidal height difference measurements is
N = GEOID HEIGHT
HB = ∆h - ∆N + HA
h = ELLIPSOIDAL HEIGHT
based on several factors such as GPS receiver
h=H+N
manufacture type, observation session duration, and the
measured baseline distance, but it does not depend greatly
on prior knowledge of the absolute vertical position of
Figure 1. Geoid/Ellipsoid Relationship
either occupied station. Dual frequency, carrier phase
measurement based GPS surveys are usually able to
produce 3-D relative positioning accuracies under 30 mm
b. Geoid height values at stations where either only
at the 95% confidence level over baseline distances less
h or H is known can be obtained from geoid models
than 20 km, depending on the type of GPS surveying
which are mathematical surfaces representing the shape
method used. This situation exists mainly because GPS
of the Earth's gravity field. The geoid model is
range biases are physically well correlated over relatively
constructed from a truncated functional series
short distances and tend to cancel out as a result of
approximation using a spherical harmonics expansion
forming double differences for carrier phase data
and an extensive set of globally available gravity data.
processing. In contrast, GPS absolute code positioning
The model is determined from the unique coefficients of
accuracy will contain the full effects of any GPS range
the finite series representing the geoid surface. Its
measurement errors. The method explained below to
accuracy depends on the coverage and accuracy of the
obtain NAVD88 elevations from satellite surveys is
gravity measurements used as boundary conditions.
based on the relative vertical positioning capability of
Former geoid models produced for general use limit
GPS.
absolute accuracies for geoid heights to no less than 1
meter. More recent geoid models have shown a
b. Geoidal height differences describe the change in
significant increase in absolute accuracy for geoid heights
vertical position of the geoid with respect to the ellipsoid
to a few centimeters.
between two stations. These relative geoidal heights can
be more accurate than the modeled absolute separation
c. In practice the shape of the geoid surface is
values within extended areas because the relative geoidal
estimated globally as a function of horizontal coordinates
height accuracy is based on the continuous surface
referenced to a common geocentric position. Specific
characteristics of the geoid model, where only small
geoid height values are extracted from the model surface
A-2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
