ETL 1110-2-367
31 Mar 95
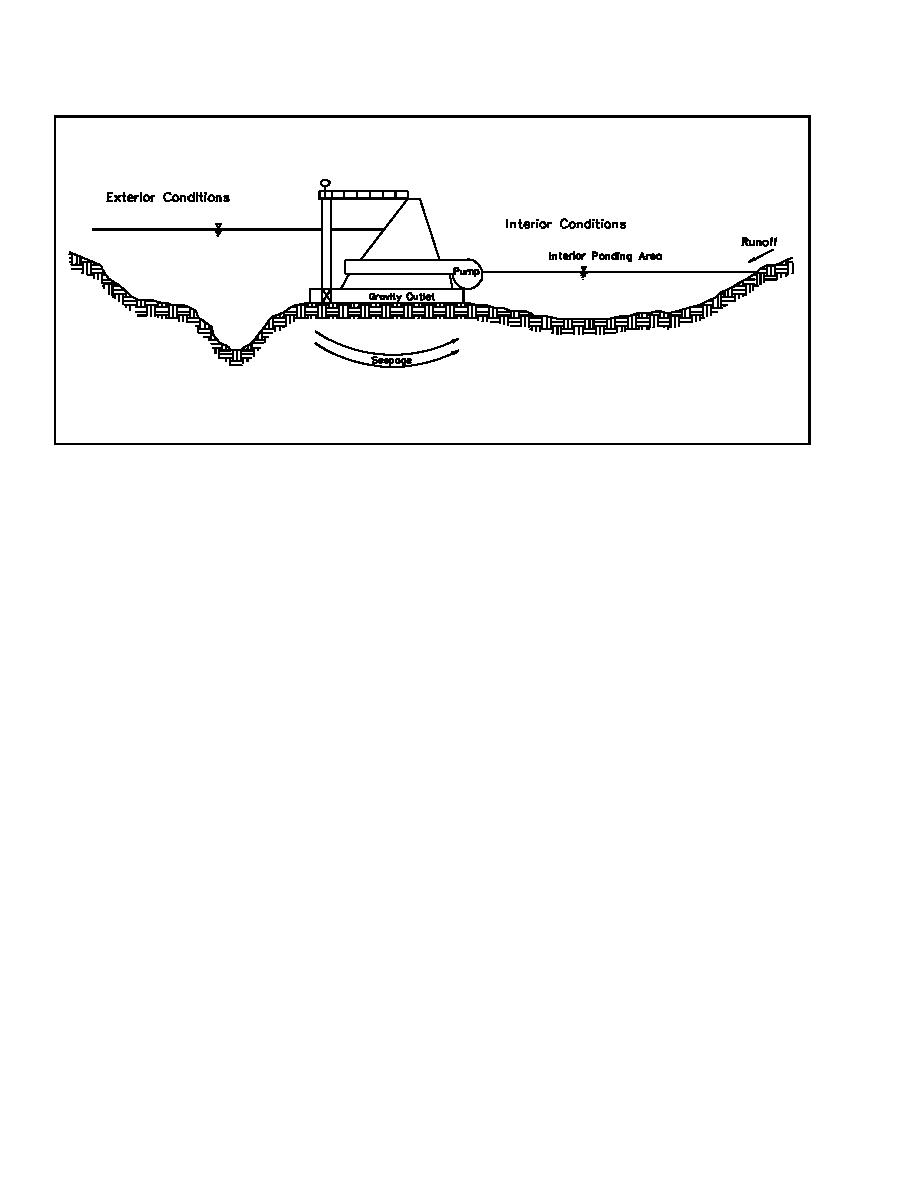
Figure 1-2. Cross section of typical interior system
as any flood reduction measure: to strengthen the national
agreements. They can represent a significant proportion of local
economy, enhance the environment, promote social well-being,
costs, especially operation and maintenance costs.
and foster regional development. The plan selected for
1-3.
Organization of Document
implementation is the one that best meets these objectives.
a. This document follows the technical steps necessary to
f.
Hydrologic analysis of interior areas is complex and
successfully conduct a flood damage reduction analysis for
often difficult. Records may be scant or nonexistent, land use
interior areas. Hydrologic engineering aspects, data collection
(and thus runoff) may have changed and is often continuing to
requirements, and evaluation of a minimum interior facility for
change, natural flow paths are altered, and coincident flooding
interior areas are discussed. HEC-IFH modular concepts, data
is the common situation (coincident flooding is discussed in
input procedures, and evaluation of with- and without-project
paragraphs 2-6 and 2-7). Interior areas are generally flat and
conditions are also discussed. The main document provides
small (less than 2.59 sq km or 10 sq miles) and the measures to
information on:
be considered are numerous, making the analysis tedious. The
HEC-IFH program makes the technically complex problem of
(1)
Study strategy.
interior flooding easier to analyze.
g. Interior area investigations are different from other
(2) General analysis procedures when beginning an
interior analysis.
studies by hydrologic analysis factors and the uniqueness of
commonly implemented flood damage reduction measures. But
(3)
Concepts and applications of the HEC-IFH program.
the study process and types of studies conducted to plan and
design flood damage reduction actions are identical to those of
(4) Preliminary investigations of the study area and data
other Corps investigations. Interior area analysis must follow
assembly.
current federal planning and design policies and regulations.
Analysis includes formulation and evaluation procedures, level
(5) Analysis of existing and future without-project
of protection considerations, and hydrologic, economic,
conditions for evaluating a minimum facility evaluation.
environmental, and social assessment criteria.
h. Interior area planning studies are an essential aspect of
(6) Analysis of interior flood damage reduction measures
to determine the appropriate gravity outlet, pumping and
feasibility studies. Although facilities and costs may at times be
detention storage capacity.
small components of a major line-of-protection project, the
elements are often major items in the negotiated local sponsor
1-2



 Previous Page
Previous Page
