ETL 1110-2-367
31 Mar 95
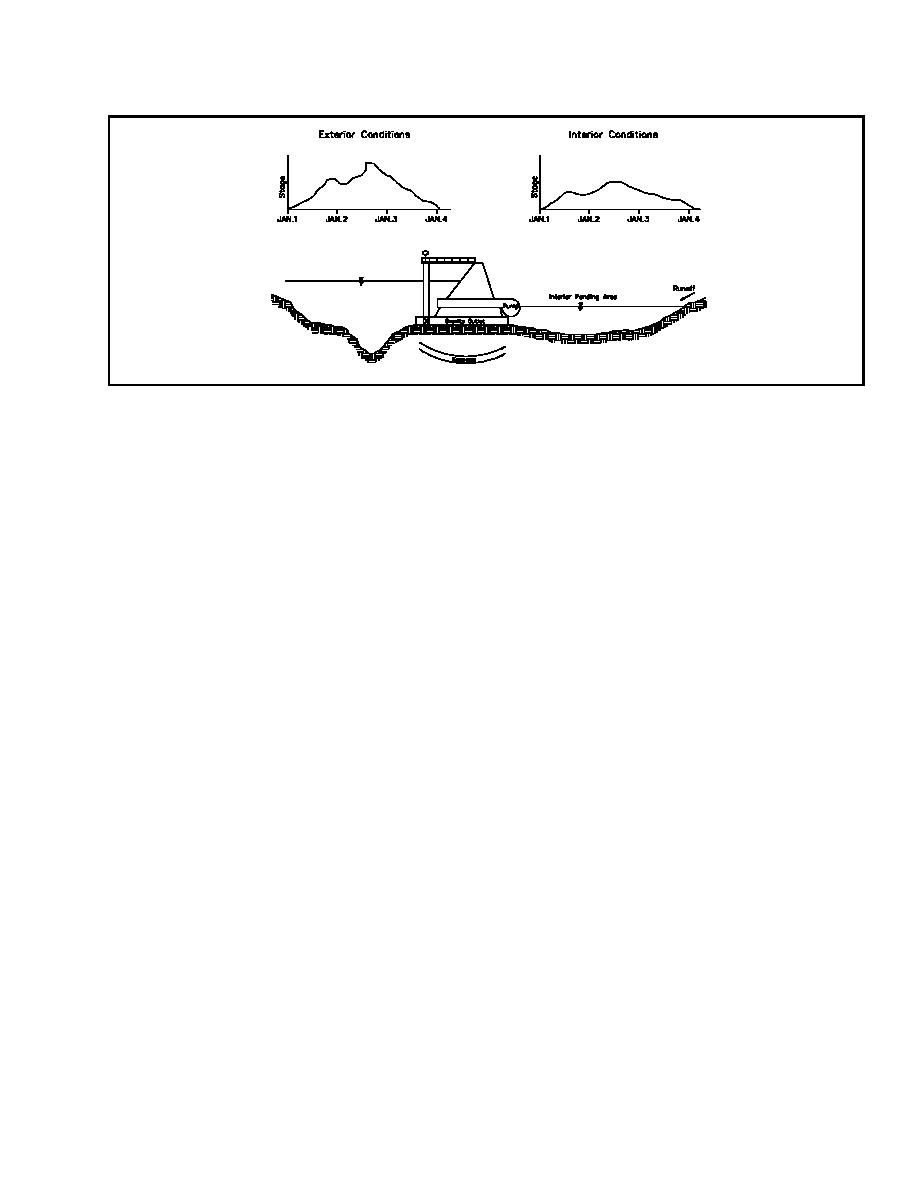
Figure 2-2. HEA concepts for dependent events
discharge hydrographs are computed using the same method
Short historic records may be unrepresentative with respect to
described for the interior discharge hydrographs. The exterior
giving good estimates of more rare events or combinations of
stage hydrograph is then defined by applying the exterior
events. Thus, 30 to 40 years of record may be inadequate to
discharge hydrograph to a rating curve at the interior ponding
derive stage-frequency results for rare events (1- to 0.2-percent
area primary outlet.
events). For this situation, the CSA method should be used to
define the more frequent events and the HEA method to help
(2) Hypothetical analysis for independent events. This
determine the rarer events. The resulting frequency relationship
procedure is applicable when floods affecting the interior area
may be a product of both approaches.
can be independent of floods that affect the exterior stages.
2-8.
Summary
These areas are often relatively small interior areas located
along large rivers, lakes, or coastlines. One probabilistic
Hydrologic analysis techniques used in planning studies of
procedure applicable to the analysis of independent events using
interior areas vary in analytical concepts and procedures.
hypothetical rainfall is the coincident frequency method,
Unfortunately, the analysis is usually tedious and complex.
conceptualized in Figure 2-3. This method applies the total
Selection of techniques should be based on the type and phase
probability theorem to generate stage-frequency functions for
of the study; complexity and relative importance of the
interior areas affected by various combinations of interior and
coincident nature of flooding at the outlet; complexity of the
exterior flooding. Figure 2-4 defines the steps necessary to
hydrologic system; the nature of the flood damage,
perform the coincident frequency procedure.
environmental, and social factors pertinent to the study area; and
the experience of the analyst. The two techniques presented
(3) HEA applicability and limitations. HEA requires less
here are the continuous simulation approach and the
data than the continuous record technique. The analysis
hypothetical event approach; several variations exist with each.
generates hypothetical frequency hydrographs in which the peak
When working on a study, one should try to use everything
flow rate, runoff volume, and all durations are assumed to be
available from both methods. For example, the CSA may be the
statistically consistent with the percent chance exceedance
best method to use on a particular study; however, the
assignment of the rainfall events. This method overcomes the
continuous record precipitation is so short that an HEA analysis
potential lack of data problems of CSA. However, for many
is needed to include the larger, rarer events. To get the
study settings, interior and exterior flooding are not totally
minimum and maximum range of interior stages, an analysis of
dependent or independent.
both totally blocked and unblocked conditions is also
c.
Using both CSA and HEA. Often continuous record
recommended.
data are available, but the number of years of record is short.
2-5



 Previous Page
Previous Page
