ETL 1110-2-560
30 Jun 01
The failure rate of a series system is equal to the sum of the failure rates of its components. This is true
regardless of the failure distributions of the components.
b. Mission reliability. The mission reliability model uses the actual system configuration to measure
the system capability to successfully accomplish mission objectives. The mission reliability model may
be series, parallel, standby redundant, or complex.
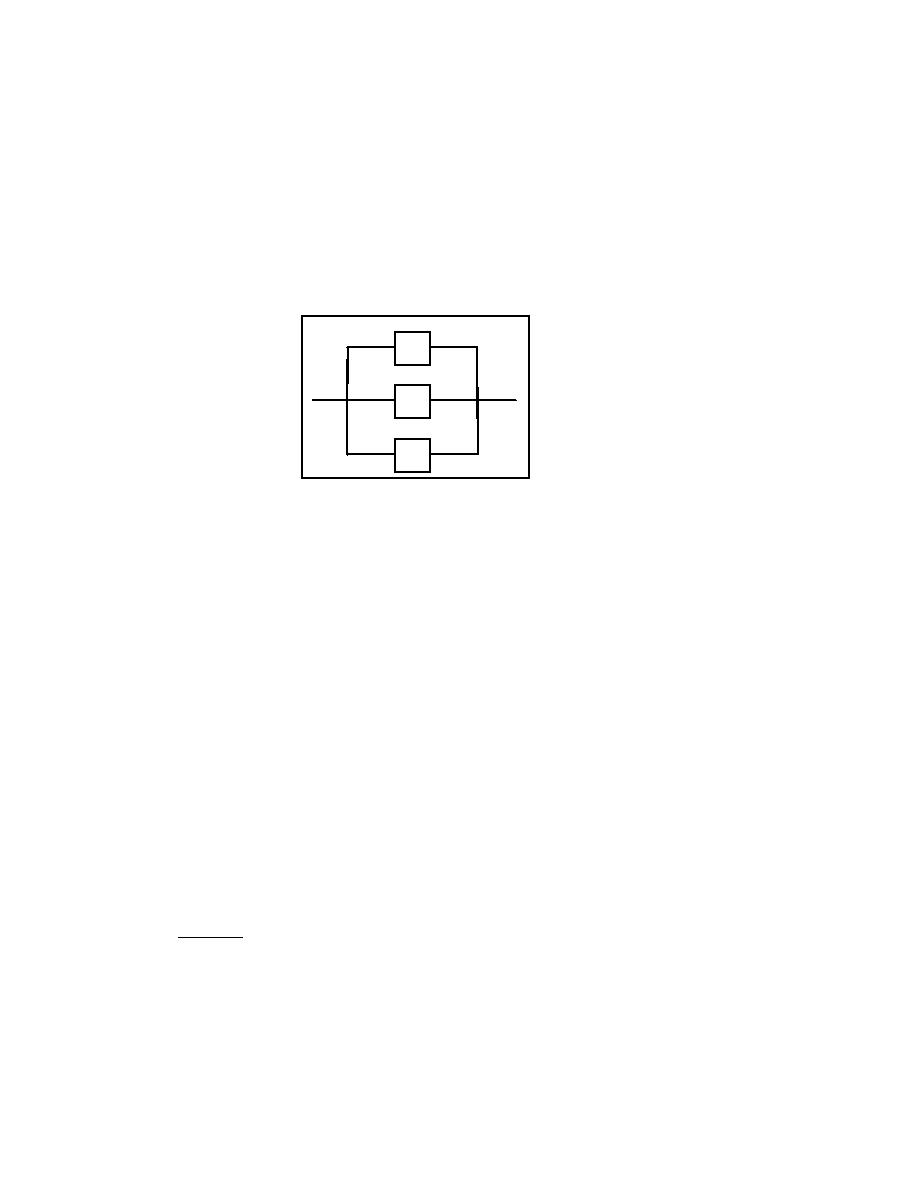
(1) Parallel system model. In a parallel system, the system fails only when all of the components
fail. Such a system is represented in Figure 7. In this configuration, the system will still perform if at
least one of the components is working.
A
B
C
Figure 7. Parallel System
The reliability for the system is given by
RS(t) = 1 [1 - RA(t)][1 - RB(t)][1 - RC(t)]
(12)
or,
N
∏
RS(t) =
[1 - Ri(t)]
(13)
1-
i =1
A more general form of a parallel system is the "r out of n" system. In this type of system, if any
combination of r units out of n independent units arranged in parallel work, it guarantees the success of
the system. If all units are identical, which is often the case, the reliability of the system is a binomial
summation represented by
n
n
∑
R(t)j [1 - R(t)]n-j
RS(t) =
(14)
j
j =r
where
n
n!
=
(15)
j
j!(n - j)!
The hazard rate for parallel systems can be determined by using
9



 Previous Page
Previous Page
