ETL 1110-1-175
30 Jun 97
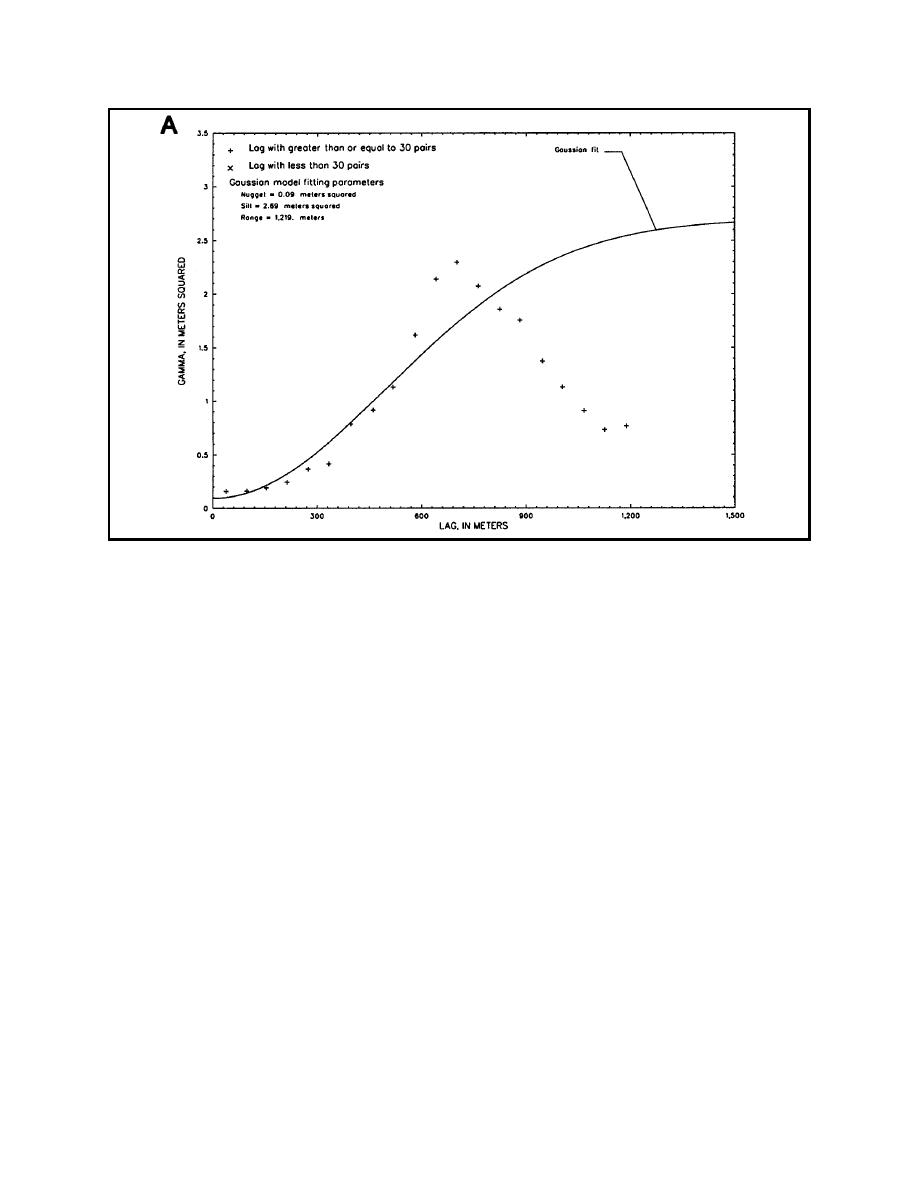
Figure 5-2. Variogram and variogram cross-validation plots for residuals in water-level example--A, theoretical
variogram; B, cross-validation scatterplot; C, cross-validation probability plot (Sheet 1 of 3)
g. To use the kriging standard-deviation
kriging estimates for all points in a 26-by-26 grid
with a grid size of about 61-by-61 m. A gray-
values in a more quantitative manner, the investi-
scale map of the kriging water levels is shown in
gator needs to establish some assurance that the
Figure 5-3a and basic univariate kriging estimate
measured data and the reduced kriging errors are
statistics are listed in Table 5-2a (water level A).
approximately normally distributed and also that
The kriging results a are a good representation of
the assumption of stationary residuals after drift
the results from other more elaborate studies.
removal is correct. If the investigator is confident
about these assumptions, then the basic statistical
f. Kriging standard deviations for the kriging
principles involving confidence intervals can be
estimates are shown in Figure 5-3b. The magni-
applied. In this example, the standard deviation of
tude of kriging standard deviations can provide
about 0.35 throughout most of the map indicates
investigators with a direct indication of where the
that there is a 95-percent chance that the true value
uncertainty associated with kriging estimates is
at a location where there is a kriging estimate will
relatively high or low. The areas of greatest uncer-
be within about 0.70 (twice the kriging standard
tainty for the kriged water levels are in the upper
deviation) of the kriging estimate.
right and lower left corners of the map, where
standard deviations are as high as about 1.4 and
0.8. Not surprisingly, these areas are where the
density and the accuracy of kriging estimates, two
density of the measured data is relatively low.
new maps were developed. To make the first map,
Throughout much of the remainder (about 70 per-
a decrease in network density was effected by
cent) of the map, the kriging standard deviation is
removing nine measured locations from the north-
almost constant at about 0.35.
west part of the area (Figure 5-1b) where sampling
5-5



 Previous Page
Previous Page
