ETL 1110-2-367
31 Mar 95
(2) RUNOFF module. Interior runoff hydrographs may be
simple percentage of the rainfall. It is normally used in
computed or imported from an external HEC-DSS file. HEC-
agricultural areas with daily time intervals and where a
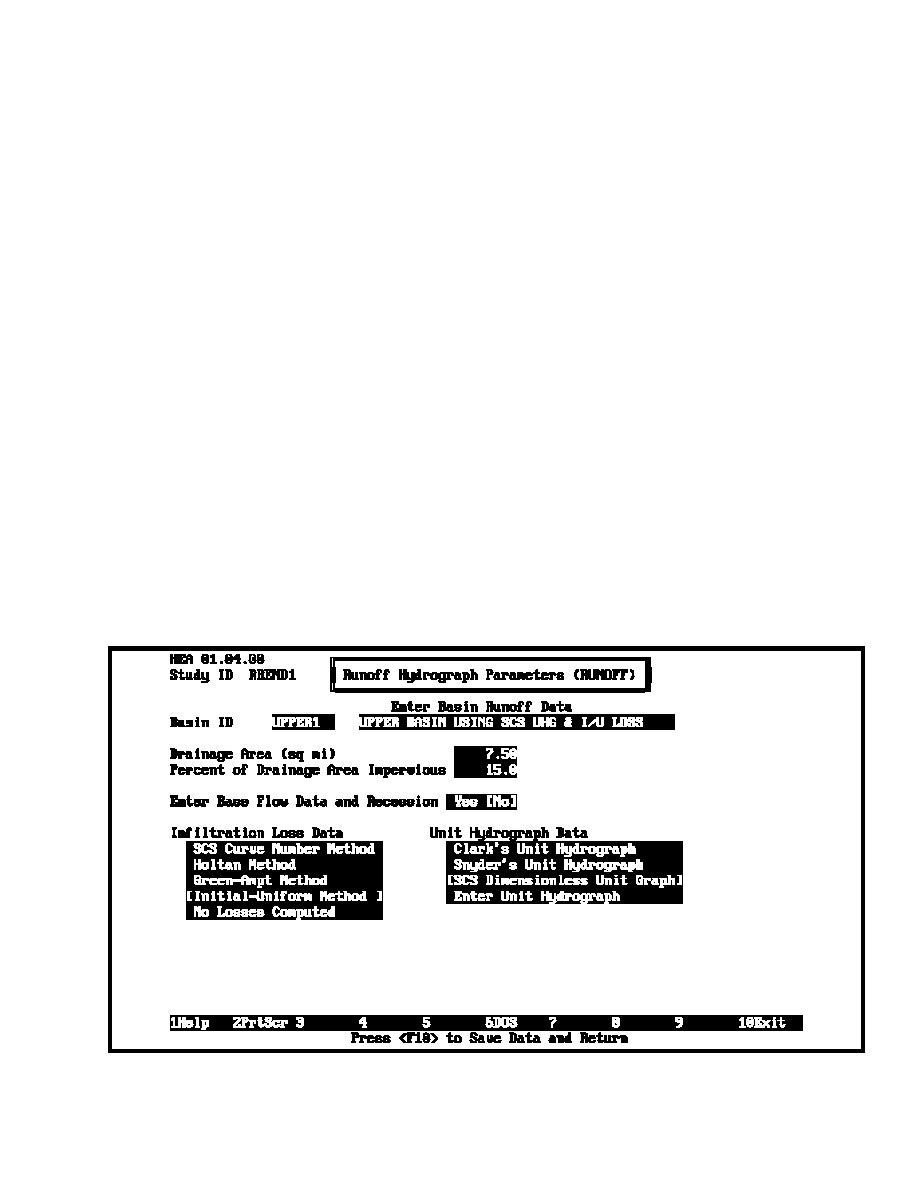
IFH subbasin runoff parameters include data entry for basin
significant amount of interior ponding exists. The initial-
characteristics, unit hydrographs, and loss rates. Data entry for
uniform-recovery is used for most continuous analyses
channel routing between the upper and lower subbasins is also
performed by HEC-IFH and includes a simplified method of soil
included. Figure 3-11 shows a typical subbasin runoff data
moisture accounting.
entry screen. The program is limited to two interior subbasin
areas per analysis.
HEA loss options are the SCS Curve Number, Holtan, Green-
Ampt, Initial-Uniform Methods, and no loss. The method used
(a) Basin characteristics. The subbasin drainage area and
is largely a user preference based on calibration studies and
percent imperviousness are entered.
reasonableness of runoff volumes.
(b) Unit hydrograph. The user may select Clark's, Snyder's,
(d) Base flow.
Continuous simulation analysis can
or Soil Conservation Service (SCS) unit hydrographs or enter a
incorporate monthly rates for base flow. Hypothetical event
unit hydrograph directly. A plot of a typical unit hydrograph
analysis can incorporate an initial base flow rate and recession
used by HEC-IFH is shown in Figure 3-12.
variables similar to the HEC-1 program.
(c) Loss rates. Loss rate methods and parameter values
(e) Streamflow routing. HEC-IFH has four routing
include monthly rates for continuous record analysis and event
techniques: simple lag method with no flow attenuation,
rates for hypothetical event analyses. Often an adequate
modified Puls, Muskingum, and Muskingum-Cunge methods.
representation of the flood volumes is more important than peak
The simple lag, the modified Puls, and the Muskingum methods
flows. Because of this, estimates of the loss rate parameters can
can be used in either CSA or HEA. Muskingum-Cunge is only
be more critical than unit hydrograph and stream routing
available in HEA. Modified Puls requires a storage versus
parameters into HEC-IFH, as illustrated in Figure 3-8. HEC-
outflow relationship and the number of routing steps.
IFH enables users to select several loss rate options. CSA loss
Figure 3-13 shows the data entry screen for channel routing. An
options are generalized runoff coefficients, initial-uniform-
HEC-IFH plot of a modified Puls storage versus outflow
recovery method, and no losses. The generalized method is a
relationship is illustrated in Figure 3-14.
Figure 3-11. Subbasin runoff data entry
3-9



 Previous Page
Previous Page
