ETL 1110-1-163
30 Jun 96
B-3. S-B Slurry Walls
borings should be logged by a qualified geologist or
geotechnical engineer. Surveys should also be
performed to determine the exact location of any
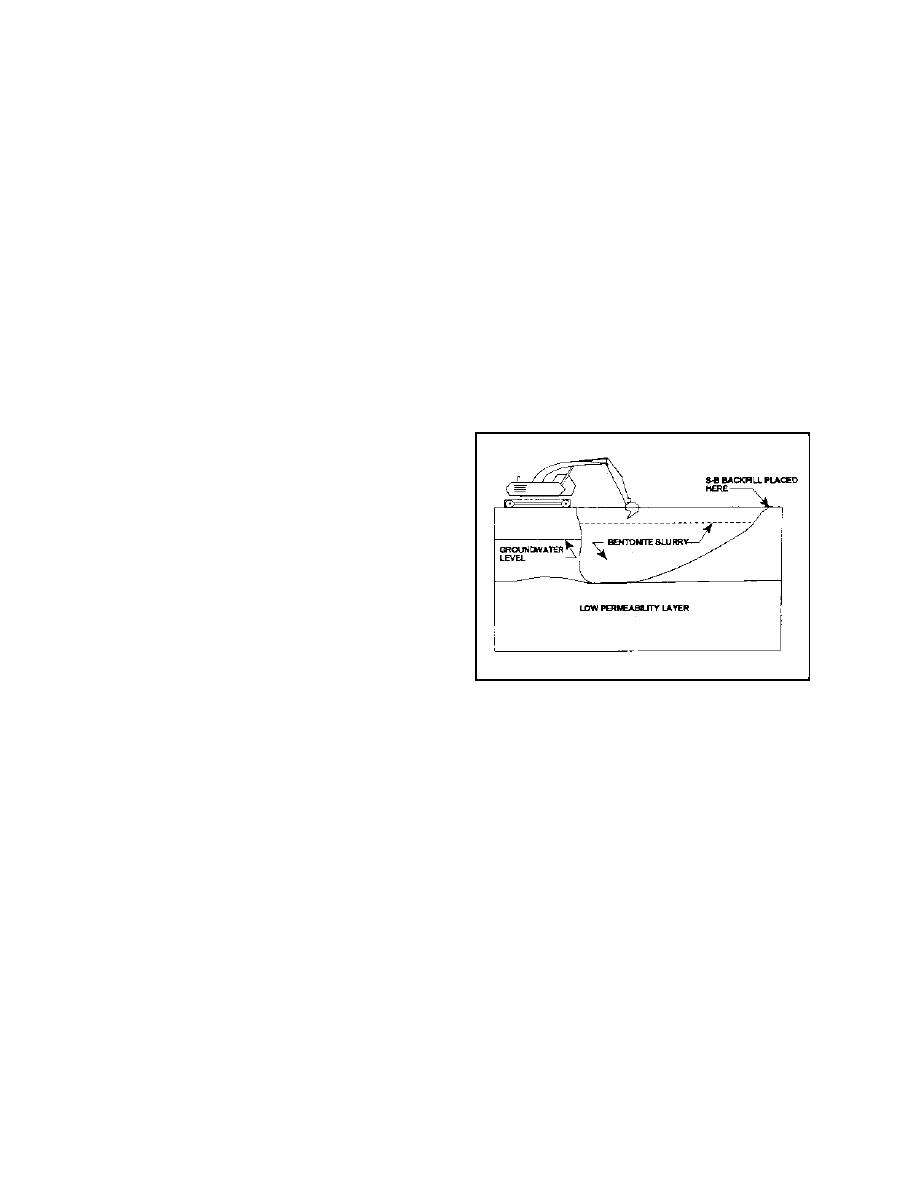
a. History and background. A S-B slurry wall
geotechnical investigations used to define the bound-
(Figure 1), constructed by the slurry trenching
ary of the contaminated area.
technique, is a subsurface barrier made to impede or
redirect the flow of groundwater. This technique was
(2) Site geology. The subsurface geologic con-
pioneered in the United States in the mid-1940's
ditions must be determined and understood prior to
using technology developed by the oil industry.
design and construction of a vertical barrier wall.
Slurry wall construction is a versatile technique that
Some of the geologic data which may be required for
has been used extensively for cutoff walls in dams
design include detailed site stratigraphy, soil or rock
and levees, and is very successful in controlling pol-
type, grain size distribution, Atterberg limits, moisture
lutants, contaminated groundwater, and landfill
content, chemical properties of the aquifer materials,
leachate migrating from waste sites. Because they
degree of weathering, structural discontinuities, rock
have been so successful, the use of slurry walls has
hardness, and rippability.
largely replaced the use of traditional cutoff barriers
such as steel sheet pile walls and grout curtain walls
(3) Hydrology. In addition to understanding the
at hazardous waste sites.
geology, it is imperative to have an understanding of
the site groundwater conditions to define pollution
migration paths. The types of hydrologic information
typically required for design include the following:
location of the water table, recharge and discharge
zones, hydraulic head distribution, hydraulic conduc-
tivity, porosity, extent of geologic units, contaminants
present in the groundwater, and background water
quality. After data gathering has been accomplished,
potentiometric surface maps, geologic cross-sections
with water table elevations, and the depth and extent
of the slurry wall can be determined. A groundwater
model can be used to evaluate and simulate future
groundwater conditions, and several vertical barrier
wall alignments can then be evaluated by the model.
Figure 1. Slurry wall schematic
d. Chemical data requirements. Chemical test-
ing is often required for the features listed below. A
chemist should be involved in these aspects of the
b. General construction. A S-B slurry wall is
project.
constructed by excavating a narrow vertical trench,
typically 600 to 1,500 mm (2 to 5 ft) wide, through
(1) Leachate and groundwater testing.
pervious soils to a relatively impervious key stratum.
During excavation, the trench is filled with slurry
(2) Determination of limits of waste.
consisting of a bentonite and water mixture. The
trench is kept full of slurry to prevent the trench
(3) Contaminated materials handling.
walls from caving or sloughing. The slurry also
develops a filter cake on the walls of the trench that
(4) Compatibility testing of vertical barrier wall
contributes to trench stability and to the low perme-
materials and site contaminants.
ability of the completed cutoff wall. Slurry trenches
have been excavated to depths of more than 30 m
(5) Borrow soil testing (contamination check).
(100 ft) with no caving or sloughing of the trench
B-3



 Previous Page
Previous Page
